
The Library Importer offers a minimalist Simple interface mode where the selected database and file-based component libraries are imported to Workspace components through a single step, while the importer automatically takes care of type classification, the target source folder, parameter inclusion and value type, and the transfer of all relevant data. The interface to this process – the Library Importer – presents a one-click solution that automatically analyses the selected libraries and imports them to the Workspace to which you are actively connected.Ĭatering for all types of libraries, relating to older component management methodologies (SchLib, PcbLib, IntLib, DbLib, SVNDbLib), the Library Importer is a dedicated solution for quickly building your company's Workspace component library so you can benefit from their many advantages – high-integrity, centralized storage and management, ease of design reuse, real-time supply-chain information. (The folder name was the same as in English in the older versions of Microsoft Windows.Altium Designer, in conjunction with your connected Workspace, provides a streamlined and highly automated process to quickly import your existing libraries to that Workspace. Program Files ( Program Dosyaları (x86) for WoW64) Program Files ( Pliki programów (x86) for WoW64)
Program Files ( ملفات البرامج (x86) for WoW64)Ĭhinese (Simplified, Traditional, Taiwan)
#WINDOWS COMMONS FOLDER DESIGNER WINDOWS#
When this virtualization is enabled for a process, Windows saves changes to the 'Program Files' folder to %LocalAppData%\VirtualStore\Program Files (x86). Windows Vista addressed this issue by introducing File and Registry Virtualization. Programs that store their data in 'Program Files' will usually not run correctly on Windows NT systems with normal user privileges unless security is lowered for the affected subdirectories. Those operating systems had no file system security, and programs could therefore also store their data in 'Program Files'. This can be an issue for programs created for Windows 9x. If Windows is installed on an NTFS volume, by default, the 'Program Files' folder can only be modified by members of the 'Administrators' user groups.
#WINDOWS COMMONS FOLDER DESIGNER INSTALL#
To be backwards compatible with the 8.3 limitations of the old File Allocation Table filenames, the names 'Program Files', 'Program Files (x86)' and 'Common Program Files' are shortened by the system to progra~ N and common~ N, where N is a digit, a sequence number that on a clean install will be 1 (or 1 and 2 when both 'Program Files' and 'Program Files (x86)' are present).

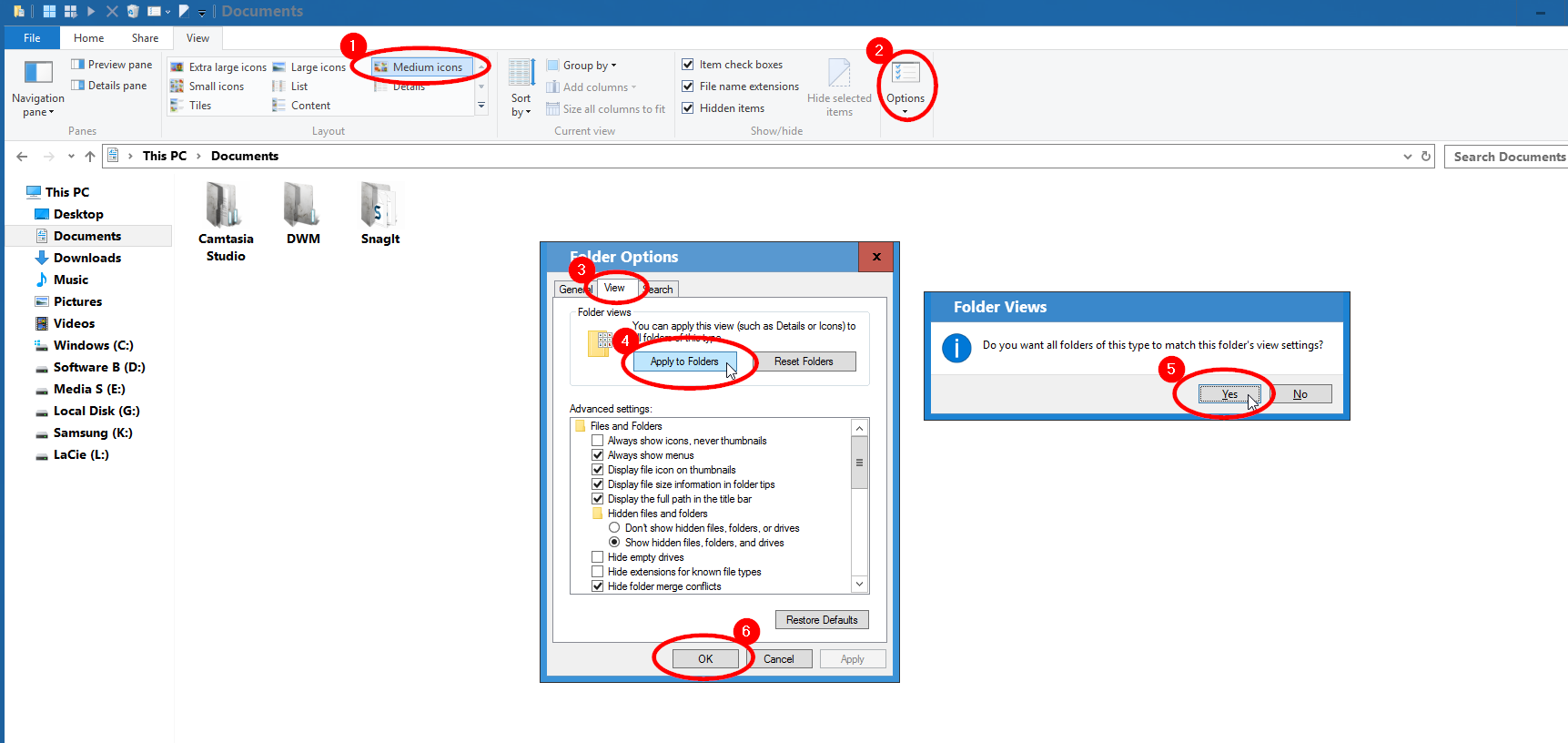
While 64-bit Windows versions also have a %ProgramFiles(x86)% environment variable, the dirids and CSIDLs are not different between 32-bit and 64-bit environments the APIs merely return different results, depending on whether the calling process is emulated or not. X86-64 and IA-64 versions of Windows have two folders for application files: The Program Files folder serves as the default installation target for 64-bit programs, while the Program Files (x86) folder is the default installation target for 32-bit programs that need WoW64 emulation layer. These are all localization-independent methods. Applications can also obtain the locations of these paths by querying the Setup API using dirids, or through Windows Management Instrumentation, or by querying the shell using CSIDLs, or ShellSpecialFolderConstants. They are then made accessible to the rest of the system via the volatile environment variables %ProgramFiles%, and %CommonProgramFiles%. At system startup, the actual paths to 'Program Files' and 'Common Program Files' are loaded from the Windows registry, where they are stored in the ProgramFilesDir and CommonFilesDir values under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion. Additionally, the Windows shell localizes the name of the Program Files folder depending on the system's user interface display language.īoth 'Program Files' and 'Common Program Files' can be moved. Instead, the localized names are NTFS junction points to the non-localized locations.

In Windows Vista and later, the paths to the 'Program Files' and 'Common Program Files' directories are not localized on disk. In a standard Windows installation, the 'Program Files' directory will be at %SystemDrive%\Program Files (or the localized equivalent thereof), and the 'Common Program Files' (or the localized equivalent thereof) will be a subdirectory under 'Program Files'. Shared resources, for example resources used by multiple applications from one company, are typically stored in the ' Common Program Files' directory. Typically, each application installed under the 'Program Files' directory will have a subdirectory for its application-specific resources.
Program Files is the directory name of a standard folder in Microsoft Windows operating systems in which applications that are not part of the operating system are conventionally installed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
